Embarking on the journey of understanding Financial Advisor Fees Explained in Simple Terms opens the door to a realm of clarity and insight into the world of financial advice. As we delve into the intricacies of different fee structures and their implications, a clearer understanding emerges, guiding individuals towards informed decisions and empowered choices.
Exploring the nuances of financial advisor fees sheds light on the various factors that can influence costs, enabling individuals to navigate this crucial aspect of financial planning with confidence and knowledge.
Overview of Financial Advisor Fees
When working with a financial advisor, it is essential to understand the various fees that may be charged for their services. These fees can vary depending on the advisor's fee structure, investment approach, and level of service provided. By being aware of these fees upfront, clients can make informed decisions about their financial planning.
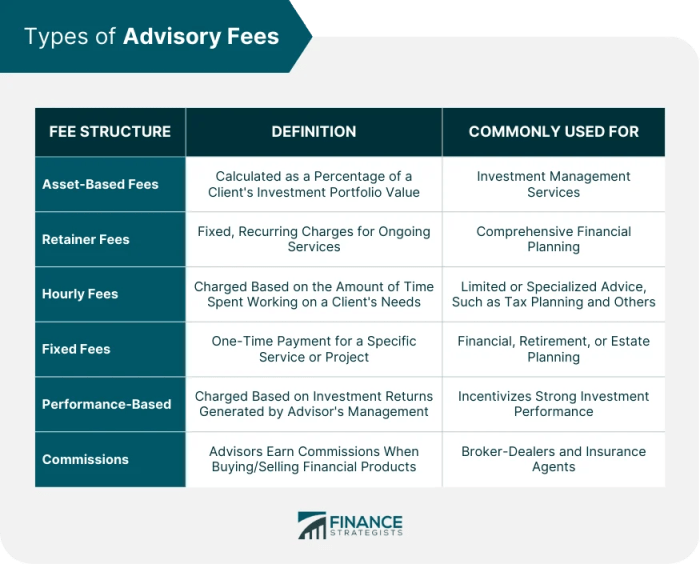
Types of Financial Advisor Fees
- Asset-based fees: These fees are calculated as a percentage of the assets under management. For example, an advisor may charge 1% of the total assets they are managing for a client.
- Hourly fees: Some advisors charge an hourly rate for their time spent working on a client's financial plan or providing advice. This can range from $100 to $400 per hour, depending on the advisor's experience and expertise.
- Flat fees: A financial advisor may charge a flat fee for specific services, such as creating a financial plan or conducting a portfolio review. This fee is typically agreed upon upfront and does not change based on the client's assets.
- Commission-based fees: In some cases, advisors may earn commissions on financial products they sell to clients. This can create potential conflicts of interest, as advisors may recommend products that generate higher commissions for themselves.
Variability of Financial Advisor Fees
Financial advisor fees can vary significantly based on the advisor's fee structure and the level of service provided. For example, a fee-only advisor who charges a flat fee for financial planning services may have different pricing than an advisor who charges a percentage of assets under management.
It is crucial for clients to understand how their advisor's fees are structured to determine the total cost of working with them.
Importance of Understanding Advisor Fees
Understanding financial advisor fees is crucial for clients to assess the value they are receiving and ensure transparency in the advisor-client relationship.
By knowing how fees are structured and the potential costs involved, clients can make informed decisions about their financial goals and choose an advisor whose fee model aligns with their needs and preferences.
Types of Financial Advisor Fees
When it comes to financial advisor fees, there are three main types to consider: fee-only advisors, fee-based advisors, and commission-based advisors. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which can impact the recommendations and advice provided by advisors.
Fee-Only Advisors
Fee-only advisors are compensated solely by the fees paid by their clients. They do not earn any commissions or incentives for selling specific financial products. This fee structure is often seen as more transparent and unbiased, as the advisor's recommendations are not influenced by potential commissions.
Fee-Based Advisors
Fee-based advisors charge a fee for their services, but they may also earn commissions from selling certain financial products. This hybrid fee structure can sometimes create a conflict of interest, as advisors may be tempted to recommend products that result in higher commissions, even if they are not the best option for the client.
Commission-Based Advisors
Commission-based advisors earn their income through commissions on the financial products they sell to clients. While this fee structure may seem attractive due to potentially lower upfront costs for clients, it can lead to biased recommendations, as advisors may prioritize products that pay higher commissions over those that are truly in the client's best interest.
Factors Affecting Financial Advisor Fees
When it comes to understanding financial advisor fees, there are several key factors that can influence how much you'll pay for their services. These factors can vary based on the complexity of your financial needs, the advisor's experience and expertise, as well as their location.
Complexity of Financial Needs
The complexity of your financial situation plays a significant role in determining the fees charged by a financial advisor. If you have intricate investment portfolios, multiple income sources, or complex estate planning needs, the advisor may need to dedicate more time and resources to develop a comprehensive financial plan for you.
As a result, you can expect to pay higher fees for their specialized services.
Advisor's Experience, Expertise, and Location
The experience and expertise of a financial advisor can also impact their fee structure. Advisors with advanced certifications, specialized knowledge in certain areas, or a proven track record of successful client outcomes may command higher fees due to the value they bring to the table.
Additionally, the location of the advisor's practice can influence their fees, as advisors in metropolitan areas or high-cost regions may charge more to cover their operating expenses and maintain profitability.
Tips for Evaluating Financial Advisor Fees
When it comes to evaluating financial advisor fees, it's essential to understand the different fee structures and factors that can influence the costs. By following a step-by-step guide and being aware of common red flags, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial advisor fees.
Additionally, knowing how to negotiate or discuss fees with a financial advisor can help ensure a fair and transparent fee arrangement.
Understanding Fee Structures
- Start by understanding the various fee structures commonly used by financial advisors, such as flat fees, hourly rates, asset-based fees, or commission-based fees.
- Consider which fee structure aligns best with your financial goals and the level of service you expect from your advisor.
- Compare the total costs associated with each fee structure to determine which option offers the most value for your specific financial situation.
Identifying Red Flags
- Be wary of advisors who are not transparent about their fees or who are hesitant to provide a breakdown of costs.
- Watch out for advisors who push high-cost investment products or strategies that may benefit them more than you.
- Avoid advisors who guarantee high returns or promise quick profits, as these could be signs of potential fraud or unethical practices.
Negotiating Fees with Your Advisor
- Openly discuss your concerns about fees with your advisor and ask for clarification on any costs that seem unclear.
- Consider negotiating a lower fee based on the level of service you require or the amount of assets you plan to invest.
- Be prepared to walk away if you feel the fees are too high or if the advisor is not willing to negotiate a fair rate.
Closure
In conclusion, the exploration of Financial Advisor Fees Explained in Simple Terms serves as a valuable tool for individuals seeking financial guidance. By demystifying the complexities of fee structures and offering insights into evaluation strategies, this discussion equips readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions and secure their financial future with confidence.
FAQ Section
What are the different types of financial advisor fees?
Financial advisors typically charge fees in various forms such as fee-only, fee-based, and commission-based.
How do fee structures impact the advice provided by advisors?
The fee structure can influence the recommendations given by advisors, as it may align their interests with the client's needs.
What factors can affect financial advisor fees?
Key factors include the advisor's experience, expertise, location, and the complexity of the client's financial needs.
How can individuals evaluate financial advisor fees?
Individuals can evaluate fees by comparing different advisor charges, watching for red flags, and negotiating fees with advisors.